Data
Last updated on 2025-01-07 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 60 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I include data in my package?
Objectives
- Learn how to use the
datafolder.
Packaging data
In some situations, it could be a good idea to include data sets as part of your package. Some packages, indeed, include only data.
Take a look, for instance, at the babynames package.
According to the
package description, it contains “US baby names provided by the
SSA”.
In this chapter we will learn how to include some data in our package. This can be very useful to ship the data together with the package, in an easy to install way.
Is your data too big?
Packages are typically not larger than a few megabytes.
If you need to deal with large datasets, adding them to the package is not an advisable solution. Instead, consider using Figshare or similar services.
Using R data files
R has its own native data format, the R data file. These files are
recognizable by their extensions: .rda or
.RData. Using R data files is the simplest approach to data
management inside R Packages.
Step 1: let R know that you’ll use data
We can add data to our project by letting the package
usethis help us. In the snippet below, we generate some
data and then we use usethis to store it as part of the
package:
R
example_names <- c("Luke", "Vader", "Leia", "Chewbacca", "Solo", "R2D2")
usethis::use_data(example_names)
What happened?
Type and execute in your console the code we just showed. What does it do? Does it require any further action from our side?
It provides a very informative output. Probably you’ll see something like this:
OUTPUT
✔ Setting active project to '<working folder>/mysterycoffee'
✔ Saving 'example_names' to 'data/example_names.rda'
• Document your data (see 'https://r-pkgs.org/data.html')So, what happened is that it created the file
example_names.rda inside the data folder.
Additionally, it activated the project, but that’s not very relevant
because most likely the project was already active.
The last element in the list shows something that
didn’t happen: the data documentation. Actually, we are
asked to do it ourselves. usethis is kind enough to provide
us with a link with further information, in case we need it.
So let’s move to the second (and last) step, and document our data.
Step 2: document your data
Everything you put inside your package needs some documentation. Data is no exception. But, how to document it? The answer is easy: not very differently as did with functions in the documentation episode.
An example documentation string for our data could be:
#' Example names
#'
#' An example data set containing six names from the Star Wars universe
#'
#' @format A vector of strings
#' @source Star Wars
"example_names"We will save this text in R/example_names.R, and we are
ready to go.
Checking that everything went ok
In the build panel, press install and restart. Now, type
?example_names in the console. Do you see some information
about the dataset?
Tip: if not, make sure that you activated
Generate documentation with Roxygen in the
Build/More/Configure build tools tab.
Using raw data
Sometimes you need to use data in formats other than
.rda. Examples of this are .csv or
.txt files.
In order to store raw data in your package, you have to follow a slightly different procedure. Namely:
- Create a folder
inst/extdata/, and save files there. Note that a user will have access to these data. - When loading the data, do not describe the path as you usually would. Instead, use something like:
R
filepath <- system.file("extdata", "names.csv", package = "mysterycoffee")
names <- read.csv(filepath)
Discussion
When do you think is it useful for a package to include data that do
not have the .rda or .RData extensions?
Having files without the R extensions is useful when one of the main purposes of the package is to read external files. For instance, the readr package loads rectangular data from files where the values are comma- or tab-separated.
Summary
Data handling inside R packages can be a bit tricky. The diagram below summarizes the most common cases:
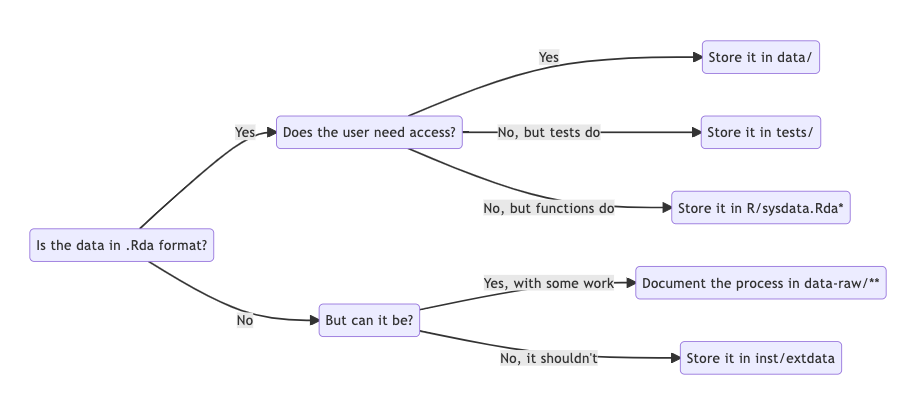
The diagram was created with mermaid. This is the original code:
flowchart LR
id1(Does the user need access?) --Yes--> id6(Store it in data/)
id3(Is the data in .Rda format?)--Yes--> id1
id1 --No, but tests do--> id5(Store it in tests/)
id1 --No, but functions do--> id4(Store it in R/sysdata.Rda*)
id3 --No--> id8(But can it be?)
id8 --Yes, with some work --> id9(Document the process in data-raw/**)
id8 --No, it shouldn't--> id7(Store it in inst/extdata)*) R/sysdata.Rda is a file dedicated to (larger) data
needed by your functions. Read more about it here.
**) data-raw/ is a folder dedicated to the origin and
cleanup of your data. Read more about it here.
If you need further help, please take a look at section 14.3 of the excellent R Packages tutorial by Hadley Wickham.
Key Points
- R packages can also include data
